3D printing is a technology that is gradually changing our world. It allows you to create complex and unique objects from various materials, from plastic to metal. Recently, several innovations have appeared that significantly expand the possibilities of 3D printing and make it even more convenient and affordable.
Advanced and new structures

Benefits of generative design include the ability to create complex and streamlined structures that can only be produced with 3D printing. This reduces the weight and improves the performance of products such as automotive parts or components for the aerospace industry.
It's also worth noting that 3D printing has the potential to eliminate the need to keep large stocks of spare parts. Instead, companies can print the parts they need as needed, which is cost effective and reduces waste.
Overall, the new possibilities of 3D printing continue to attract attention and applications in various industries. They open the door to innovation, improvement and new possibilities in production and design. As technology advances and new materials emerge, we can expect even more progress and amazing results in the future.
Production and design on request

On-demand production with 3D printing also saves on costs. Traditional production methods require large investments in equipment and infrastructure, as well as long production line setup times. In contrast, 3D printing allows you to quickly create and modify prototypes and products without the need for large investments.
With the ability to create complex structures and optimize parts, 3D printing also improves product performance and efficiency. For example, companies can create lighter weight car parts, resulting in lower fuel consumption and improved environmental performance.
Prostheses

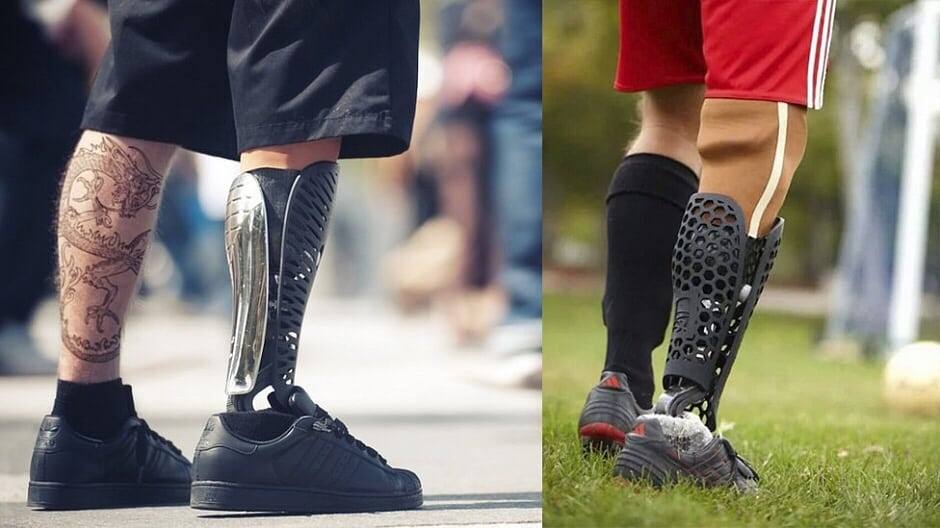
3D printing of prostheses has changed the situation, making them affordable and more cost effective. Various kinds of prostheses have been developed by the 3D printing community, including limbs, facial prostheses, and even animals. Customized prostheses can be designed by scanning and simulating the patient and then printed using available printers and materials.
3D printing also allows the creation of lighter and stronger prostheses, such as William Root's leg exoprosthesis, by exploiting the hollow internal geometry of the structure. 3D printed prostheses are constantly evolving thanks to volunteers and open source. Engineers, scientists and volunteers around the world are collaborating to create innovative prostheses never before available to amputees. Organizations such as Ayúdame3D also provide poor people in developing countries with prostheses they could not otherwise afford.
Innovation

Startup Psyonic, for example, is using additive manufacturing to create sensory prosthetic hands. They supply their prostheses not only to amputees, but also to the US military, Apptronik and Meta. Projects like these take bionics from science fiction to reality, and Psyonic isn't the only company innovating.
e-Nable is a volunteer organization that is changing lives by revolutionizing the way prostheses are designed and distributed. They help volunteers and individuals 3D print better and more affordable prostheses and donate them to people in need. They have a variety of designs to suit different types of amputees, including designs for specific tasks, such as a 3D-printed bow holder that allows a person born without fingers to play the viola.
3D printing is also finding applications in veterinary medicine. Veterinarians have saved the life of an endangered bird by 3D printing a prosthetic beak after being diagnosed with cancer. Other veterinarians are using 3D printing to create innovative surgical instruments for veterinary operations.
Thus, 3D printing of prostheses not only makes them affordable and cost-effective, but also opens up new opportunities for innovation and improving the lives of people and animals.
Audiology

What could be more individual than the shape of each person's ear? Naturally, 3D printing has sparked a flood of innovations in audiology, both for medical hearing aids and consumer headphones.
Waiting times for hearing aids are being reduced as medical devices can be 3D printed for patients as soon as they receive their prescriptions. They can also be custom printed to fit the patient's ear, or aesthetically tailored to the patient's style if they complain about looking like their grandfather.
These innovations don't just benefit the hearing impaired. Workers in hazardously noisy workplaces (such as Formula 1 racetracks) are ordering special 3D printed ear plugs to fit their ears perfectly to reduce the risk of any noise leaking out.
Have you ever listened to a song and the music disappeared due to an earpiece falling out? Your kids won't get as irritated thanks to companies like Sennheiser that print custom-fit perfectly-fitted headphones.
These innovations are not just about customization, cost, or speed; The world's smallest hearing aid has been 3D printed, bringing technology to new miniature sizes. And this does not only apply to wealthy people. Hearing aids can be 3D printed in remote locations for as little as $1, making them more accessible worldwide.
Accomodation

Construction, printed on a 3D printer, is rapidly developing around the world. While China and the United Arab Emirates pioneered the technology with several exciting projects, you can now find 3D printed designs all over the world!
Whether you want to rent a 3D printed house on Airbnb in Canada, rent a 3D printed house in the Netherlands, or move into a fully 3D printed apartment building in Germany, you can do it in 2023! There are even several 3D printing houses on the market to buy if you want to take your enthusiasm for 3D printing to the next level. As you read this, an entire neighborhood of over 3 houses is being 100D printed in Texas!
There are many reasons why 3D printing is the next big thing in construction, but nothing is more important than cost and time savings. Habitat for Humanity is already helping low-income families move into 3D-printed homes.
While the aforementioned projects are owned by innovative 3D printing companies like COBOD, Icon, and Alquist, they are far from the only ones operating in the industry.
The materials from which these houses are built are as innovative as the concept and technology. From branded concrete and mortar to local ground materials such as sand, mud or rice waste, there are materials to suit every homeowner's taste and environmental considerations. Ancillary companies such as Branch Technology are even innovating using 3D printed scaffolding. They use free-form 3D printers to create stronger yet lightweight structures that can be used as-is or filled with low-cost materials to create on-demand cases or reinforced structures.
Organs, tissues and drugs

It's only a matter of time before 3D printed organs join our new reality of skull and vertebral implants. Several promising projects are already in development. Right now, the technology is limited to tissue cultures like those created by Carnegie Mellon University researchers that use hydrogels and “components” of organs like heart valves. Researchers have created 3D-printed living tissues, and in some cases they have even been successfully implanted into laboratory animals. Human trials are only a matter of time.
Startups such as Prellis Biologics are already 3D printing tissue models, vascular channels and tissue scaffolds. These capillary tissues are vital for the functioning of organs, and the innovative capillary bioprinting technology is a major step towards the production of fully 3D printed organs. They achieve this by using holographic technology to simultaneously project and print tissue from biological material.
3D printed fabrics are also changing the way drugs are tested. Cells behave differently in 3D cultures, making them inaccurate approximations to living 3D tissue cultures, a long-standing problem solved by 3D printing. 3D printing isn't just for tests: the FDA has already approved one XNUMXD-printed drug, and several pharmaceutical companies are rushing to markets with XNUMXD-printed drugs.
Extraterrestrial construction and rockets

Companies like Icon are adapting their construction printing technology to 3D print structures on the Moon and Mars using local materials for each. They have already successfully completed the Mars Dune Alpha project to 3D print a 1700 sq. feet at the Johnson Space Center in Texas to simulate a realistic habitat on Mars. Currently, astronauts use it to repeat three one-year missions to the surface of Mars before getting on with the actual work.
Icon isn't the only one looking to 3D print in space. Airbus has already sent metal 3D printers to the International Space Station in hopes of setting up a plant to manufacture orbiting satellites. They want to use abandoned space debris combined with 3D printing technology to create the next generation of sustainable satellites. There are even other construction companies claiming the Moon, such as AI Space Factory's Lina project, which aims to build bases at the Moon's South Pole, also using materials naturally found on the Moon.
Back on Earth, startups like Rocket Lab and Relativity are 3D printing the rockets they launch. They claim that 3D printing reduces the time it takes to manufacture and launch rockets into space to days. 60 years of rocket science and space travel were interrupted by 3D printing innovations in reliability, speed, flexibility and optimization. And we're not just talking about the hulls or outer layers of rockets, their engines are even 3D printed!
A new space race is underway, and 3D printing is responsible for many of the innovations that excite the astronomical community.
Spare parts for ships and cars

Thanks to 3D printers, there is no such thing as obsolescence in these high-value industries. Over the past century, many cars have been discontinued, but skilled mechanics and retro enthusiasts have worked hard to keep them running. Now scanned copies of work parts can be printed in 3D to save time.
Elvis Presley fans can thank 3D printing for fully restoring his 1958 BMW. But 3D printing is available, and not just to the rich; Specialized companies appear in the markets of classic cars that keep retro cars in working order for everyone.
It's not just land vehicles that win. Entire fleets of ships could be similarly obsolete and subject to decommissioning due to a lack of spare parts. That was until the advent of 3D printing innovations. Now giants such as Shell, the US Air Force and GE are 3D printing discontinued parts to avoid having to replace their costly fleets in need of repair.
Even non-obsolete car or boat parts can be 3D printed, and it makes economic sense for custom made fixtures. Manufacturers including Volkswagen, Bugatti, Bentley, Jaguar and BMW are using 3D printers to boost their profits.
Drones and aircraft parts

It all started with 3D printing of spare parts for drones. Then hard-working hobbyists started printing entire drones at home. Startups soon began 3D printing prototypes of their drones, including using unique and complex materials like titanium or using generative design to create life-saving drones like the X Vein. Even the military and aerospace industries have adopted additive manufacturing to innovate their designs.
3D printing is taking drones to new heights or downsizing them, as is the case with the Piccolissimo, the world's smallest autonomous aircraft. It may sound like a Black Mirror nightmare, but thanks to 3D printing, bee-sized drones could soon be swarming all around us.
3D printing allows the creation of completely sealed hollow structures. They can be lighter, stronger and more efficient than traditionally manufactured unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). This has allowed Stratasys, for example, to create a jet-powered drone, 80% of which is 3D printed. If necessary, the company says they could produce a second one within a few weeks.
The University of Sheffield has created a 3D printed drone airframe that can be printed and flown in one day. These innovative developments significantly reduce the cost of testing and production of unmanned aerial vehicles, as well as the time spent on their creation. Titomic 3D printed the titanium drone using the innovative Titomic Kinetic Fusion process, which mechanically fuses titanium powder. This innovative 3D printing method allows them to combine dissimilar metals and materials, creating parts that showcase the unique properties and benefits of different alloys in a single piece. It also eliminates welds and other imperfections that plague traditional manufacturing.
Art restoration

Great works of art that were once thought to be lost or damaged forever are given a second life thanks to 3D printing. Appendices such as fingers, legs, noses, or private parts of the body have been lost in transit or through vandalism over the hundreds or thousands of years that these statues and carvings have adorned us. Now the combination of printers, scanners and AutoCAD design is bringing these antiques back to life.
3D printing has also opened up opportunities that were previously unavailable to art lovers, climate-conscious or cash-strapped. Recreating the smallest details now allows people to see incredibly accurate reproductions of famous works of art like Michelangelo's without carbon emissions or the cost of flying to Europe. Art is for people, and 3D printing is gaining acceptance truly around the world.
The Million Image Database project assists in this task by cataloging major works of art around the world and storing them in a virtual warehouse open to anyone. Museums may be losing out on art to wealthy collectors, but people will still find a way to enjoy it.
Сonclusion
Over the past decades, 3D printing has inspired an incredible amount of innovation. The possibilities of what technology will create in the coming years may be even wider than you can imagine.
Tomorrow could see roads dominated by cars with 3D printed engines, tables filled with 3D printed food, skies filled with 3D printed drones and 3D powered aircraft. printed electronics, toy chests filled with 3D printers (if they don't already exist), 3D printed clothing (including jewelry), musical instruments, and more.
Never before have so many products been more customizable, innovative, affordable. The possibilities seem endless. With 3D printing, anyone can create the next innovation that will change lives, industries, or the world.














Author: Natalia Kamonichkina
More articles from Natalia Kamonichkina