Good afternoon, dear colleagues!
Due to frequent requests for an introduction to 3D printing technology and the ability to independently use 3D printers, I am compiling this article with a summary of what you need to know about the initial launch of 3D printing on your own site. As a site, I will consider both an apartment, office space, a garage, and specially designated areas.
At the moment, there are a lot of different 3D printing technologies. At the time of getting to know the technologies, I recommend starting with the study of 4 main technologies: FDM (FFF), LCD (DLP), SLS, SLM.
In this article, for the most part, I will focus on the first two, because equipment for the manufacture of products using these technologies is relatively affordable for purchase. The other two I will describe based on targeting the future development of your company and as a method of manufacturing products with greater accuracy, strength, wear resistance. Learn more about 3D printing technologies page.
Order a consultation Online School
Contents:
1. 3D plastic printing
2. 3D printing surface texture
3. Equipment for FDM printing
4. 3D printing with composites
5. Material shrinkage
6. 3D printing with thermosets
7. 3D printing with photopolymer resin
8. UV Resin 3D Printing Equipment
9. 3D printing with polyamides (powder)
10. Equipment for SLS printing
11. 3D metal printing (powder)
12. Equipment for SLM printing
13. Working with 3D models. Preparing for 3D printing
14. Software
15. Location of equipment installation
16. Operation and tool
17. Results
3D printing with plastic
3D printing with plastics and composite materials involves the use of FDM technologies. Layer-by-layer application of the material by extruding the polymer through a die (nozzle) and bonding the next layer to the previous one through adhesion.

At the moment, there are a huge number of manufacturers of consumables for 3D printers using FDM technology. The main thing to understand is that a polymer thread is used as a raw material, the main diameters are 1.75 mm or 2.85 mm. An example of consumable spools can be found here to register:.
The choice of material chemistry (ABS, PLA, PET-G and others) mainly comes down to the chemical and physical properties of the future product at the output. As a rule, manufacturers describe the properties of the material in the product passport or in advertising booklets describing the properties of the material. For example, our material Studia3D Filament PET-G V0 does not support combustion and has a certificate for fire safety.
3D printing surface texture
A separate factor determining the choice of consumables is the appearance of the product after manufacturing. By analogy with milling, which leaves marks from the cutter on the surface of the product, 3D printing also has its own surface texture, which resembles a stepped structure.

Different materials have their own surface texture. The surface is especially different for composite materialsThat hide layering by Infill the polymer fraction. “Stepping” or the so-called “layering” may differ not only depending on the selected material, but also on the choice of 3D printing technology, as well as depending on the selected 3D printing modes (we will talk about them later).
Surface texture of 3D printing depending on the selected technology.
| FDM technology | LCD/DLP technology | SLS technology | SLM technology |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The images above show that the FDM technology has a pronounced stepped structure, while the LCD/DLP technology contains such small layers that when printed with a transparent material, the part has a high ability to transmit light. The third image shows a polyamide product made using SLS technology. The surface texture resembles pressed flour, while the polyamide parts themselves have very serious strength. In the fourth image, a product made using SLM technology from metal powder. The surface resembles electroerosion, but with a more pronounced roughness. All 3D printing methods can be further processed. Grinding, sandblasting, polishing, shot blasting, etc. Sometimes designers make an allowance for additional machining.
Examples of application of FDM technology:
Example 1: It is necessary to print the product, based on the preliminary calculation of the strength in the CAD program. The tensile strength of the material must be at least 25 MPa at break. That is, the product must have equivalent strength in all directions, by analogy with model (molded) plastic. From an article about durability of products printed on a 3D printer we know that parts have unequal strength in all directions. The direction parallel to the laying of the layers can bear a greater load than the direction transverse to the laying of the layers. Therefore, in our case, it is necessary to select a material that will have a tensile strength across the stacking of layers higher than the required tensile strength. Specifically, in this task, PET-G plastic can be used. This polymer has very good sinterability between layers. The adhesion between the layers is so high that the difference in tensile strength along the lay and across the lay of the yarns is minimal. When breaking, the fracture surface spreads randomly, and not along the laying of the thread, as, for example, in ABS plastic.

Many manufacturers of materials for 3D printing specify such parameters in the material specification, so preliminary testing is not necessary.
Example 2: It is necessary to print a product that will be further processed mechanically in order to apply a paint and varnish coating. For such a task, it is necessary to choose a material that will be well machined, because before painting there is always a process of sanding and polishing the surface.
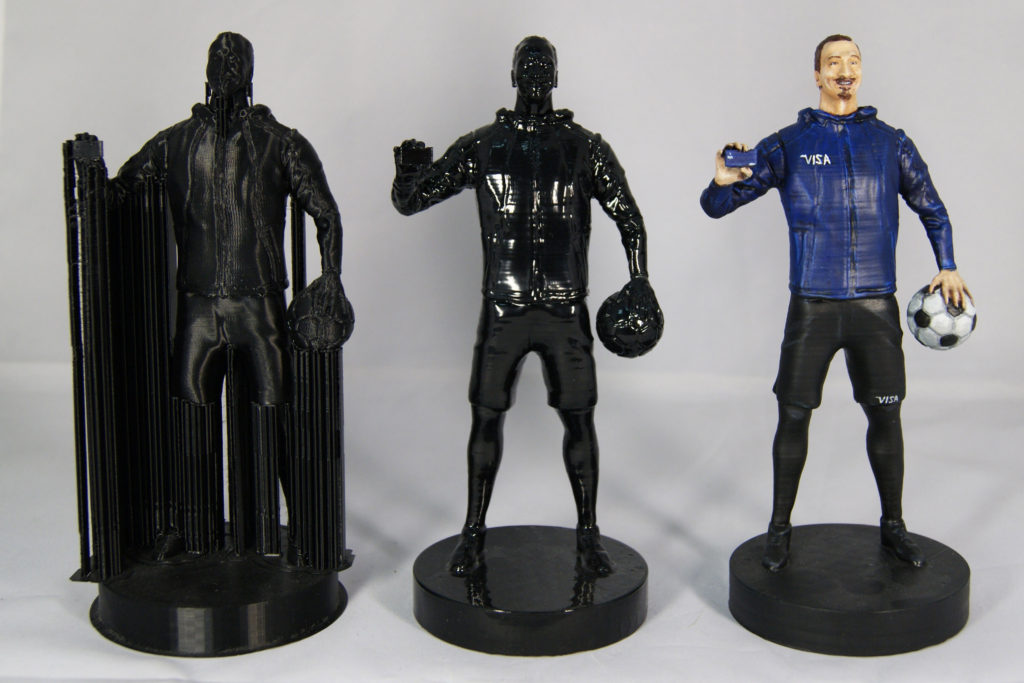

As a rule, ABS plastic is used for such tasks, however, it is worth considering that ABS plastic is easier to print on closed-type 3D printers. Next, we will analyze this point separately.
Example 3: It is necessary to print the legs for the quadcopter. It is important to understand that quadcopter legs experience relatively large shock loads, because they are in shock when the quadcopter lands, and the landing is not always soft. Therefore, we must choose a material that will be resistant to regular shock loads.

In our practice, to solve this problem, we used HIPS plastic.
Example 4: It is necessary to print a master model for removing the mold for melt casting. To solve this problem, a material is needed that will provide good burnout with a minimum ash content.
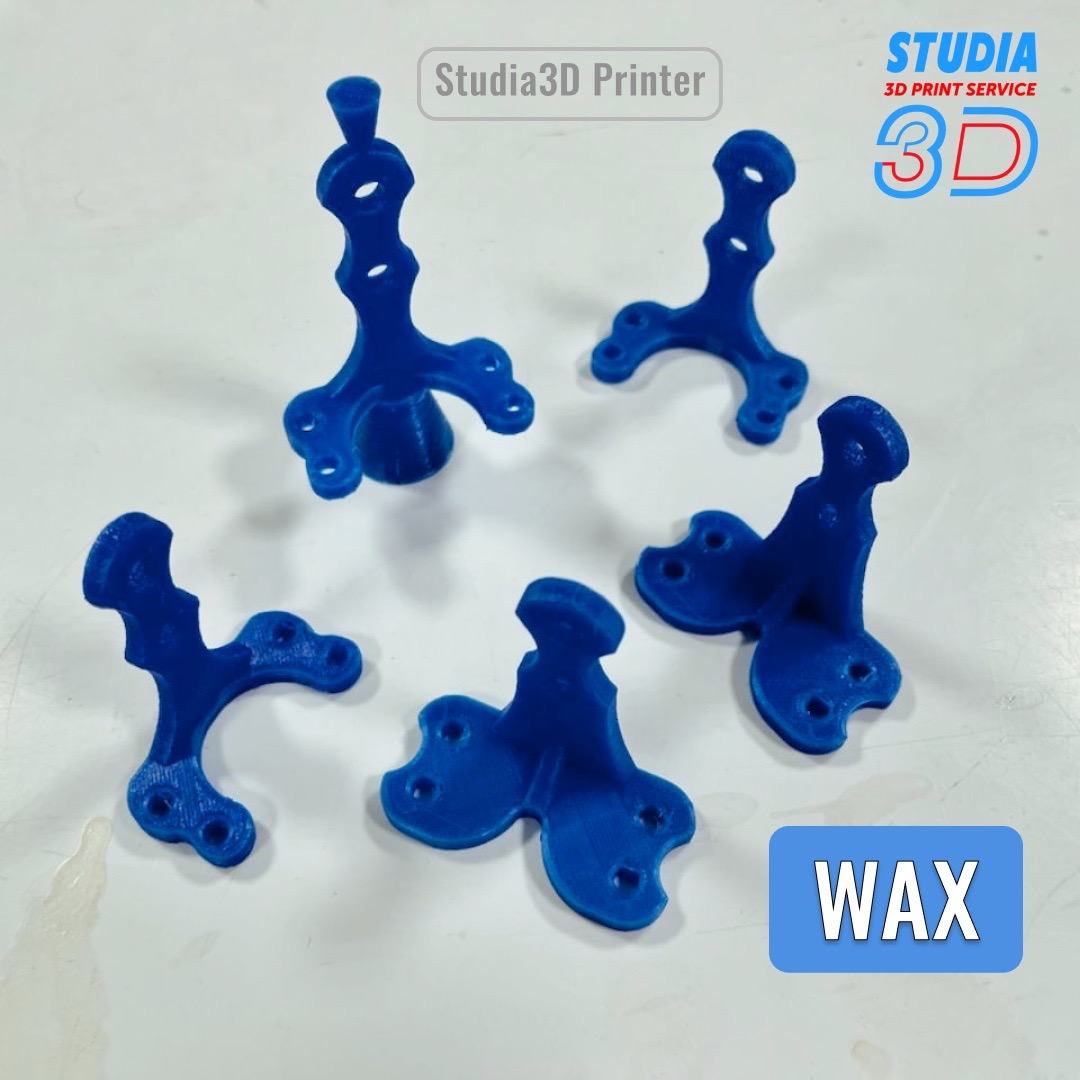

Wax is a good example of such a material.
As you can see, the use of different materials solves different problems. At the same time, the equipment for the manufacture of products remains the same. An exception may be individual nodes of 3D printers that are capable or not capable of working with certain polymers, therefore, when buying equipment, you should always check with the supplier about the possibility of printing with certain thermoplastics or the possibility of upgrading to expand the list of supported materials.
More examples of plastic printing can be seen page.
Equipment for FDM printing.
One of the things to consider when buying an FDM printer is the type of 3D printing camera. There are printers with open and closed camera types.
| closed chamber | open chamber |
 |
 |
A big misconception for most beginners is that the closed camera type of a 3D printer provides more rigidity. In fact, the closed type of the 3D printer chamber provides its own micro-climate inside the chamber and the absence of drafts, which allows you to work with plastics that have a strong shrinkage. And industrial 3D printers even have additional air heating inside the chamber. Before buying a 3D printer, you need to make sure that the material that you plan to use on this 3D printer does not shrink, and if it does, then consider buying a printer with a closed camera type.
In our practice, we have developed an approach to work on open-type 3D printers, since they are usually cheaper. And on almost any shrinkable thermoplastic there is either a similar one without shrinkage, or composite material with minimal shrinkage, allowing you to work on an open-type 3D printer. Typical examples of open-type 3D printers are widely used in the world Creality3D Ender 3, AnyCubic Chiron and others. The cost of such printers, as a rule, does not exceed 100 thousand rubles. Such machines are not whimsical in operation and are easy to upgrade. An example of a closed type 3D printer is Picaso Designer XL PRO, Raise3D Pro2 Series etc. The cost of such 3D printers is much higher than that of open ones.
3D printing with composites
3D printing with composites using FDM technology involves the use of exactly the same equipment as described above. As a rule, 3D printing with composite materials requires the use of a special working tool. For example steel nozzle instead of brass. Or upgraded extruder head, which will be able to process composite material.

The main difference is the use of a material based on thermoplastic filled with a specific fraction as a raw material. At the same time, the equipment at the base (frame, kinematics) remains unchanged.
Example 5A: Some 3D printers have the ability to print multiple materials at the same time. One of the tasks that we needed to solve was the creation of a product with an outer shell that does not conduct current, and an internal base that should conduct current.

To print the outer shell, we used regular ABS plastic, and for the conductive base, a composite with a conductive fraction was used. Still such materials can be used for “imprinting” the traces directly into the part.
Example 6: Composite materials can also be used to manufacture products with enhanced strength or wear resistance properties.
| Carbon Fiber | fiberglass |
 |
 |
These types of composites, as a rule, include materials filled with carbon or fiberglass microfibers.
Example 7: There are composite materials, where a larger proportion of Infill is occupied by a microfraction of a metal powder, which is bound by a polymer base. We can print products from such a composite material, and then burn out all the polymer in a heating furnace. In this case, the metal powder is sintered together and a metal product with a certain degree of porosity is obtained.

Example 8: By analogy with the metal composite material, there are composite materials that use stone dust as a Infill. These composites work very well in preparation for painting, even better than ABS, while still having a good weight.

Example 9: There are materials with special additives that ensure the destruction of microbes on the surface of products.

An example of such material is biocidal material from REC.
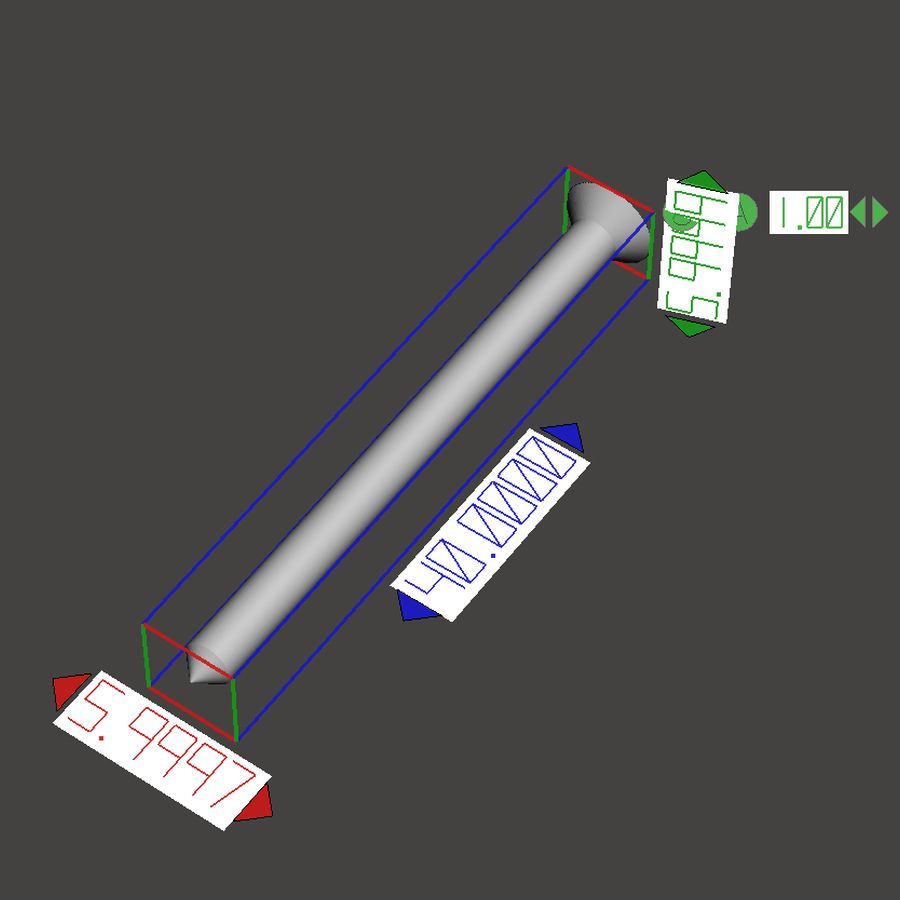
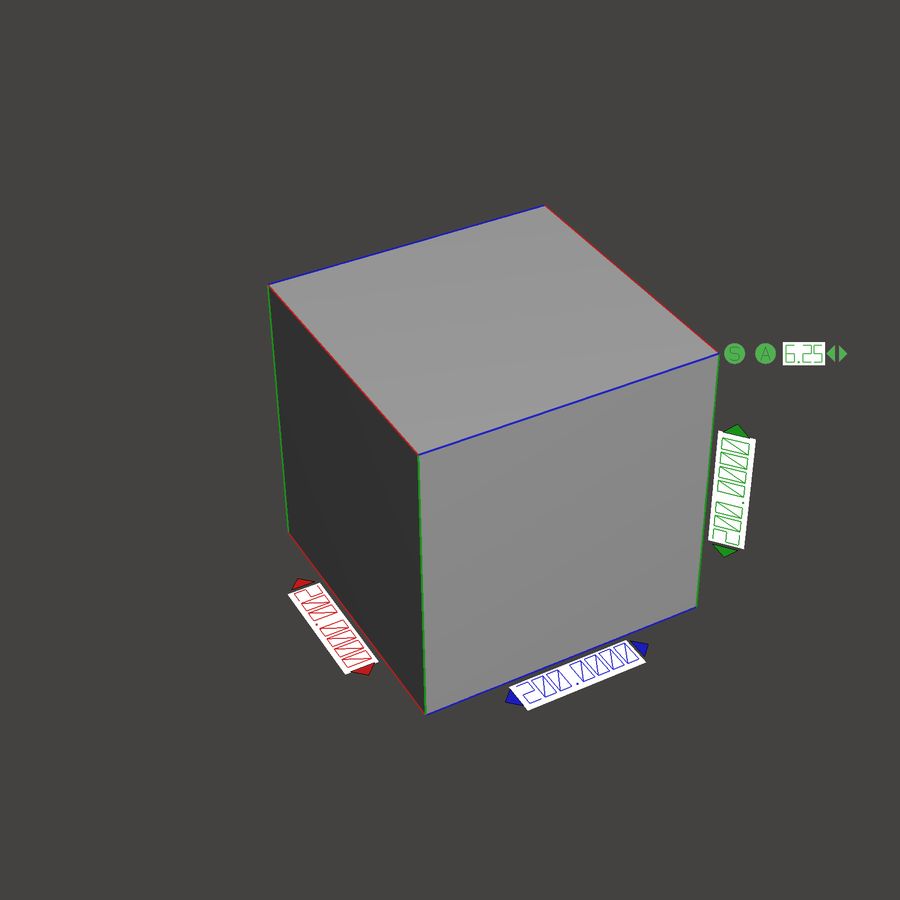
Material shrinkage
In continuation of the topic of choosing the type of camera for a 3D printer, it is necessary to take into account the fact that composite materials are very often used as an alternative to “pure” polymer due to the lack of shrinkage in the composite. For example, ABS GF4 (ABS plastic, 4% filled with glass microfibers) is an excellent analogue of regular ABS plastic. At the same time, the output product has increased strength characteristics. For this reason, we developed the concept of using cheap 3D printers with expensive materials for ourselves, and not vice versa. Expensive 3D printers can only be used in super exceptional cases, such as the use of thermosets.
An example of material shrinkage can be seen in the image below.

Choose a more expensive printer or more expensive material, everyone chooses for himself. We pursue the principle: cheap printer, expensive material. Ultimately, even in this example, it is clear that at the end we will get a product with the best characteristics in terms of strength, wear resistance, etc.
3D printing with thermosets
Rectoplasts are plastics, the processing of which into products is accompanied by an irreversible chemical reaction, leading to the formation of an infusible and insoluble material.

Thermoplastic 3D printing equipment is fundamentally no different from typical FDM 3D printers with a closed chamber. However, thermoplastics require sufficiently strong heating of the chamber. Strong camera heating implies a large thermal expansion of a large number of 3D printer components, which can lead to jamming of moving parts. Therefore, 3D printers of industrial type are used for 3D printing with thermosets. One company that manufactures such 3D printers is Stratasys. The cost of such equipment is measured in tens of thousands of dollars.
3D printing with photopolymer resin
3D printing with photopolymer resin has a surface roughness that is an order of magnitude higher in quality than FDM technology. the product at the output requires minimal processing, and most often does not require it at all.

Other differences from FDM technology are in the construction principle, the cost of raw materials (twice as high) and the need to operate in a well-ventilated area due to the strongly unpleasant smell of the material. The main factor when choosing a 3D printer of this type is the quality of the output products.
UV Resin 3D Printing Equipment
3D printing with photopolymer resin is carried out on 3D printers working on LCD, DLP, SLA technologies.
| LCD | DLP | SLA |
 |
 |
 |
The raw material for these 3D printers is UV curable resin, which is a viscous thick colored liquid. The cost of such 3D printers varies from 300 to 2 million dollars. The cost depends on the size of the construction area and the availability of additional automatic systems and sensors (auto-calibration, auto-feed of material, etc.) When choosing a 3D printer of this type, first of all, you need to look at the resolution of the radiation source. LCD 3D printers are at the first stage, for such printers it is necessary to pay attention to the expansion of the LCD matrix. The higher the extension, the higher the accuracy of the construction. At the second stage are DLP 3D printers, while it is necessary to specify the life of the projector. Very often the lifetime is shorter than the LCD matrix, but the printing is a bit more accurate. The most accurate among these technologies is the SLA technology. At the same time, the cost of SLA 3D printers is higher than those previously listed. Just like in the case of thermoplastics and composite materials, there are a huge number of consumables for photopolymer 3D printers on the market. The materials have different chemical and mechanical properties. When choosing a consumable for a photopolymer 3D printer, it is necessary to take into account the length of exposure at which the resin crystallizes.
3D printing with polyamides (powder)
3D printed polyamide SLS technologies consists in sintering polyamide powder with a laser beam. Parts made of polyamide are quite strong and have a good surface quality.

By analogy with thermoplastics and composite materials, composite powders can be used in SLS technology. Printing technology is quite expensive due to the high cost of consumables and the high cost of equipment.
Equipment for SLS printing
Equipment for 3D printing using SLS technology is mostly industrial. The dimensions of such equipment usually occupy an entire room, and sometimes an entire workshop.

At the same time, there are 3D printers of a fairly compact size, but their cost is still high, so we will not separately pay attention to this type of equipment in this article.
3D metal printing (powder)
Metal 3D printing is a technology that is unique in its essence. Parts are made according to SLM technologies. Metal 3D printing gives a wide range of options when creating the shape of a product.

Products by structure are an ideal example of a uniform fine-grained structure, which has a positive effect on the mechanical properties of parts.
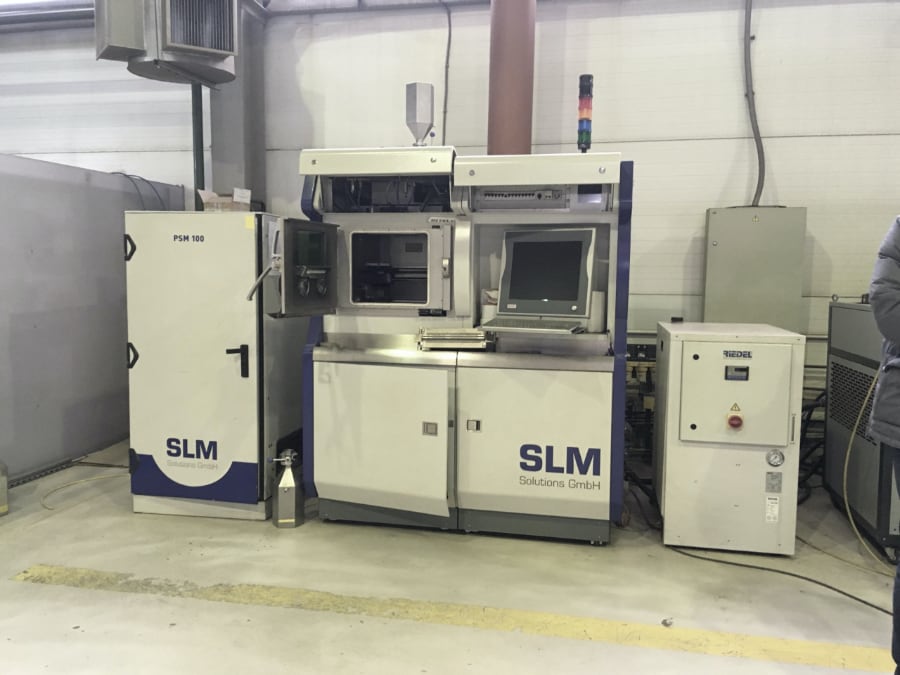
Equipment for SLM printing
The equipment is a special industrial installation, the launch requires specialized workshops, which include not only the 3D printer itself, but also additional equipment for the post-processing process, measurement and storage of consumables. The cost of such equipment is from 1 million dollars.
Working with 3D models. Preparing for 3D printing
3D printer operation algorithms are set through a 3D model by creating a control program for a 3D printer. The correctness of the algorithm depends primarily on the quality of the model preparation. What is a 3D model you can read in a separate article. It is important to understand that the 3D model must match special requirements. If you do not pay attention to these requirements, critical errors in 3D printing of a different nature.

The second very important factor in designing 3D models for 3D printing is taking into account special supporting (support) structures that are technologically important in the process of creating a product using 3D printing. The ideal option for designing products for 3D printers is a form that does not require supporting structures. You can read more about supporting structures read in the article.

Software
There are two main types of programs for working with 3D printers: for analyzing 3D models and for preparing a control program (slicers). The main programs for analyzing 3D models: AutoDesk Netfabb, Materialize Magic, Autodesk MeshMixer.
The software for preparing a control program for a 3D printer is divided into 3D printing technologies. Very often, hardware manufacturers develop their own software for their 3D printers. However, this software is not always the best choice. Therefore, here is a list of universal programs for most cases: Simplify3D, CURA, cheatbox, Lichy Slicer, Slick 3R, Prusa Slicer.

Very often, the quality of the manufactured product depends on the correct choice of 3D printing modes by changing the parameters in the control program. The main parameters that you need to pay attention to are: Infill percentage, layer height, nozzle diameter. Description of all types of parameters you can find in the article. As an example, I recommend reading the article “How are layer height and 3D print quality related?".
Location of equipment installation
Industrial 3D printers require specialized production sites, so they will not be discussed in this article. In other cases, the choice of the location of the printer primarily depends on the consumables used. Any consumable for a 3D printer has emissions into the air you breathe, so the installation location will primarily depend on whether these emissions are harmful or not. There are special ranges of materials that you can work with in direct contact, some even have a certificate for use in the food industry. In all other cases, it is necessary to take into account a well-ventilated room, and it is better to install specialized hoods. The second very important factor when choosing a location for installing a 3D printer is the noise level emitted mainly by 3D printer stepper motors. Check this parameter with the supplier, but it is better to visit the showroom first. If you are going to install a 3D printer at home, then it is best to purchase a 3D printer with minimal noise. In this case, you will hear only the noise from the fans, comparable to the noise of personal computers. In all other cases, it is better to use separate rooms with good sound insulation.

Operation and tool
During the operation of the 3D printer, you will need specialized toolwhich is better to stock up in advance. List of basic tools: latex gloves, wire cutters, pliers, tweezers, trash cans, washes, a set of hexagons and hex keys, needles for cleaning nozzles. Like any equipment, a 3D printer has consumables, which are also better to always have in stock for the smooth operation of the equipment. List of major consumable parts: nozzles, belts, platform, FEP film, die, heating block, thermistor, thermal barrier, fans, extruder and heated platform wiring kit. In the case of upgrading 3D printers, this list can be expanded.
Results
It is clear that in the text of one article it is not possible to convey all the subtleties of working with certain materials when working with a particular technology. It is impossible to convey all the experience that we have accumulated over the years. Therefore, if you have any questions, please ask them in the comments. We will try to answer all possible questions based on our experience in using 3D technologies in our own production.

















Author: Studia3D aggregator
More articles from Studia3D aggregator